
Understanding DLTs: Beyond the Blockchain Hype
Igor Benedet
Jun 29, 2025
After the creation of Bitcoin in 2009, the word blockchain spread around the world and sparked tremendous interest in the technology. With it, it’s possible to eliminate intermediaries and perform financial transactions directly between peers, with all transactions being immutable and protected by cryptography. What many people don’t know is that the Bitcoin network—just like Ethereum’s—is only one of the three possible types of DLTs (Decentralized Ledger Technology).
The Bitcoin network is a public and permissionless DLT, meaning anyone—individual or organization—can read from and write to the network. Consensus is achieved through a consensus algorithm: proof of work in the case of Bitcoin, and proof of stake in Ethereum. The public nature of these networks poses a challenge for corporate adoption, where privacy and confidentiality are often essential. The solution lies in private DLTs, with or without permissioning. A prominent example is the Hyperledger Project, from the Linux Foundation, which focuses on commercial and private DLTs for enterprise use. Let’s now dive deeper into what DLTs are and the different types available.
DLT is not a new concept. It refers to an infrastructure and set of protocols that do not rely on a central server. Each node in the network stores a copy of the ledger, and whenever a node inserts a new transaction, that change propagates across the entire network. The absence of a centralized authority to store and control the data—unlike a conventional application server—is the defining feature of this infrastructure.
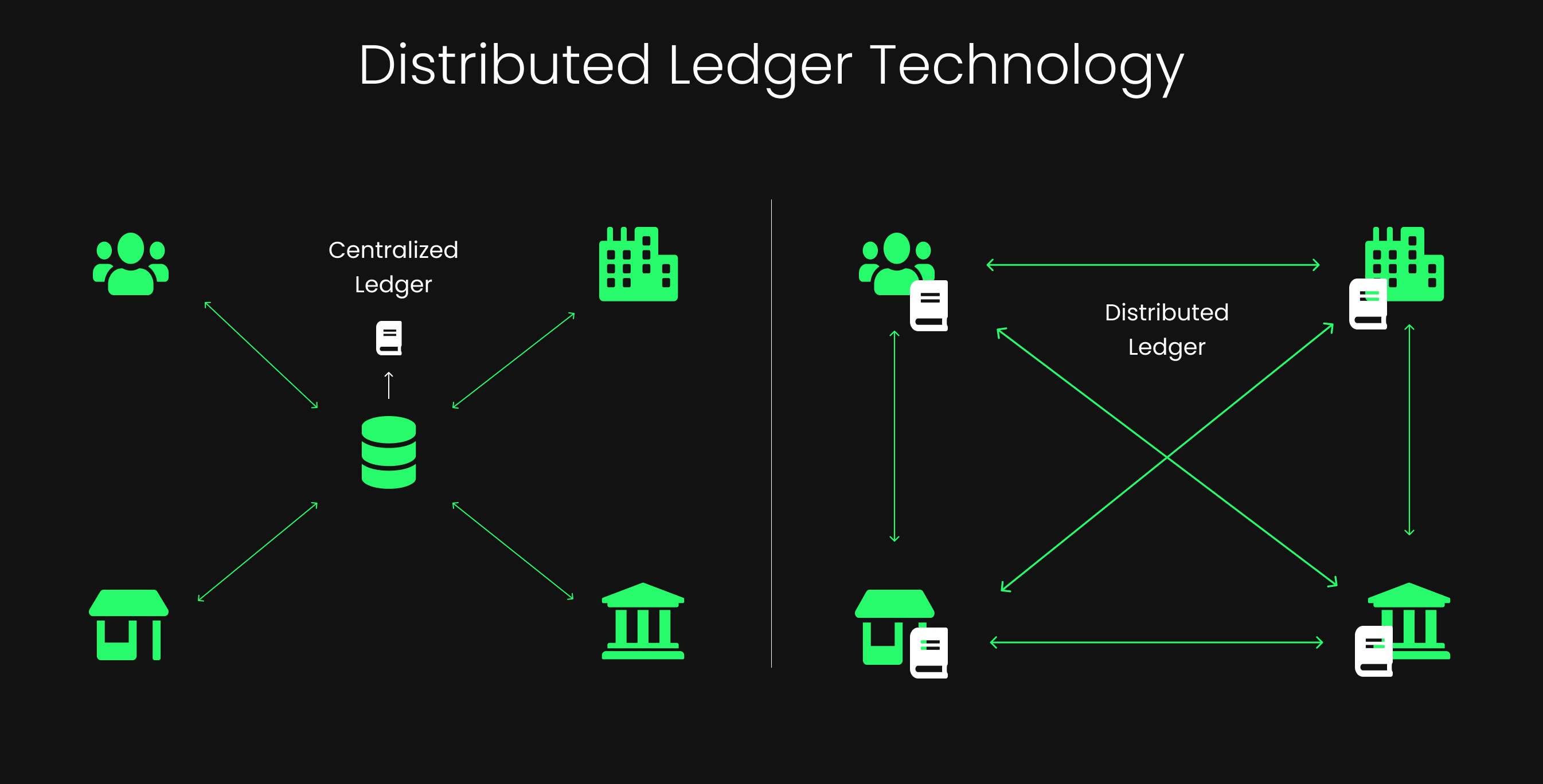
Note: All blockchains are DLTs, but not all DLTs are blockchains.
There are three main types of DLTs, each suited to specific use cases. In general, the corporate world benefits from decentralized technologies that still preserve transactional privacy between companies and entities.
Permissionless, Public, Shared Systems
These DLTs allow any entity to participate, read, and write to the network. Each node maintains a copy of the ledger, and consensus is reached via a consensus algorithm. The most well-known example is the Bitcoin network, using the proof of work algorithm. Other alternatives include Ethereum’s proof of stake model.
Permissioned, Public, Shared Systems
In this type of DLT, only authorized entities can write to the network, but all transactions remain publicly accessible. This model is especially useful in government or public transparency applications, for example.
Permissioned, Private, Shared Systems
These are DLTs in which only authorized participants can read from and write to the network. Particularly useful in corporate environments, enabling confidentiality in transactions among companies that are part of a consortium or shared network.
Hyperledger and DLT Benefits
The Hyperledger Project, by the Linux Foundation, opened the doors of distributed technology to the business world. One of its most well-known frameworks is Hyperledger Fabric, a permissioned and private platform that, according to its official documentation:
“Hyperledger Fabric is a distributed ledger technology platform, backed by a modular architecture that delivers a high degree of confidentiality, resiliency, flexibility, and scalability. It is designed to support plug-and-play implementations of various components and to accommodate the complexity and diversity that exist across the enterprise ecosystem.”
There are, therefore, technologies on the market today that enable the secure application of distributed systems in business processes, while providing all the benefits of DLTs to corporations.
According to a report from the U.S. Government Accountability Office (GAO), published in September 2019, DLT technology offers the following benefits:
- Transparency: As all nodes have a copy of the ledger and can verify transactions, the system reduces the likelihood of corruption.
- Reduced labor costs: DLT can reduce costs related to asset traceability—such as products in a supply chain—by eliminating manual tracking.
- Data quality and reliability: Transactions are generated, linked, and encrypted using computer algorithms, which can reduce human error in the process.
- Wide applicability: DLT is being applied across various sectors, including supply chain and logistics, media, energy, healthcare, and government. A notable example is Target and its ConsenSource system, which verifies whether products are sustainably sourced.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the different types and use cases of distributed ledger technologies is essential. Some may feel tempted to implement blockchain just for the hype—without carefully evaluating the real needs and costs. It's important to remember: blockchains don’t solve all the world’s problems. They are, in the end, just a technology—one that should only be integrated into business processes based on a clear and genuine need.
At Beyonders, our mission is to help companies and organizations successfully integrate distributed technologies and blockchains into their processes. Contact us through this link — and let’s go beyond!
Recent Posts

Aug 12, 2025
Release Management: How we automated this process and saved hours of work
Every software must have its own release version control, and here isnt different. In this post we will take a look in how we automated this process inside our company.

Jun 21, 2025
How Companies Are Adopting Blockchain in Their Business Processes
Discover how leading companies like Walmart, Nike, and Visa are adopting blockchain to enhance supply chains, manage digital identity, issue NFTs, and simplify international payments.

Mar 12, 2025
How to choose the right mobile app dev agency
Struggling to choose the right mobile app dev agency? Learn how to define goals, evaluate expertise, and balance cost vs. quality for a successful app!

Oct 07, 2024
Github Flow Branching Strategy
A complete and easy to use branching strategy. In this post we will go through its details and how to apply it in your repositories.
